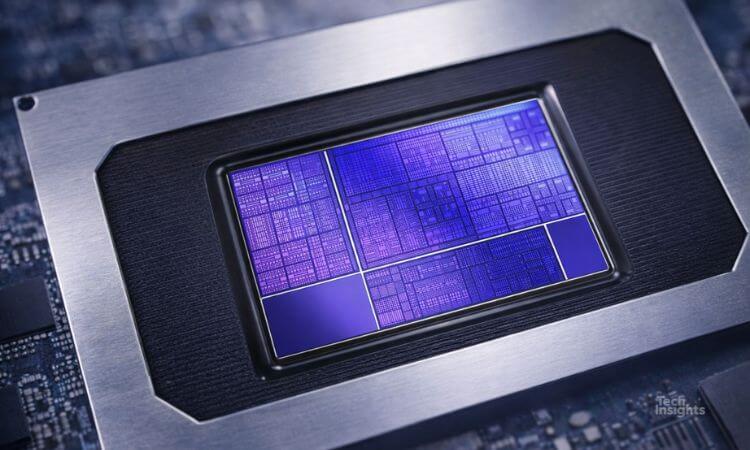
Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 in the Xiaomi Mi 11
brings a new 5 nm entrant to market
With their release of the Snapdragon 888, Qualcomm finds itself in competition with other 5 nm offerings - the Apple A14 and the Exynos 2100. With the Snapdragon 888 SoC, Qualcomm has changed foundry partners from TSMC back to Samsung.
The Snapdragon 888 SoC provides a 5 nm LPE revision to their earlier 7 nm LPP technology. By minimizing major scaling, Samsung continues to offer multiple DTCO (Design Technology Co-Optimization) benefits without the critical design rule scaling we have seen in TSMC’s N5 offering.
While Qualcomm, Apple and HiSilicon have all introduced 5 nm solutions, all of them use Arm as the basic IP block provider for their CPU and GPU implementations, and find themselves competing on the basis of differentiators - cost, performance, etc.
Early benchmarking performed by Geekbench indicates that the A14 original CPU cores boast higher performance than the Snapdragon. But an important milestone for Qualcomm has been reached regardless: the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 is the first chip in the Android world to score above the 1,000 mark in single-core performance.

TechInsights has analysis under way for this part.
In addition, we are currently analyzing the Apple A14 (and the M1) with the TSMC 5 nm process as well as the Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 with Samsung 5 nm process. And as soon as we confirm the Exynos 2100, we will kick off efforts to analyze that as well.
Find content like this and more in the TechInsights Platform. Sign-up for free today.
Tags: Qualcomm logic reverse engineering